Last Updated: January 23, 2025
For freelancers, independent contractors, and gig workers, understanding 1099 taxes can be challenging. Without the tax withholdings that traditional employees enjoy, fulfilling your tax obligations can seem like an uphill battle. However, with the right guidance and tools, managing your taxes doesn’t have to be daunting.
In this guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about handling 1099 income, from understanding tax forms and calculating payments to maximizing self-employed deductions and staying IRS-compliant. Tools like a 1099 tax calculator, and apps such as MileageWise can make the process significantly easier, saving you time and money.

Try MileageWise for free for 14 days. No credit card required!
Dashboard
Table of Contents
Understanding the 1099 Form
The 1099 form is one of the most important documents for anyone earning income outside of traditional employment. It serves as a record of payments made to you by clients, companies, or platforms and is reported both to you and the IRS to ensure transparency and accuracy.
Who Needs to Receive a 1099 Form?
If you earned $600 or more from a single client or company during the tax year, they are required to issue you a 1099 form. It’s your responsibility to report all income earned, even if you don’t receive a form from a client.
Overview of 1099 Types
- 1099-NEC (Nonemployee Compensation): The most common form for freelancers and gig workers.
- 1099-MISC: For miscellaneous income like rent, prizes, and other non-employment payments.
- 1099-K: For income processed through third-party platforms like PayPal or Stripe.
- 1099-INT: For interest income earned from banks or financial institutions.
Taxes for 1099 Earners
As a 1099 earner, you’re considered both the employer and the employee. This means you’re responsible for calculating and paying your taxes directly to the IRS. Unlike traditional employees, taxes aren’t withheld from your earnings, making it essential to understand how 1099 taxes work.
How 1099 Taxes Work
The amount consists of several elements:
- Federal Income Tax: Based on your tax bracket after deductions.
- Self-Employment Tax: A combined 15.3% for Social Security (12.4%) and Medicare (2.9%).
- State Income Tax (if applicable): Rates vary by state.
Who Needs to Pay 1099 Taxes?
You’re required to pay taxes if:
- You earn $400 or more in self-employment income during the tax year.
- Your total income meets the federal filing threshold for your filing status.
Managing Estimated Taxes
Unlike traditional employees who have taxes withheld from each paycheck, 1099 earners must pay estimated taxes quarterly. These payments cover both income and self-employment taxes.
Who Needs to Pay Estimated Taxes?
You must make quarterly payments if you expect to owe $1,000 or more in taxes when filing your annual return.
Steps to Calculate and Submit Estimated Taxes
- Estimate Your Annual Income: Include all untaxed income, such as 1099 earnings.
- Subtract Eligible Deductions: Deduct business expenses like mileage, home office use, and supplies.
- Calculate Your Tax Liability: Use tools like the 1099 tax calculator or IRS Form 1040-ES to estimate your total taxes owed.
- Divide Into Quarterly Payments: Split your total liability into four equal payments.
- Submit Payments: Pay online, by phone, or by mail using IRS Form 1040-ES.
When Are Quarterly Taxes Due?
- 1st Quarter: April 15
- 2nd Quarter: June 15
- 3rd Quarter: September 15
- 4th Quarter: January 15 (of the following year)
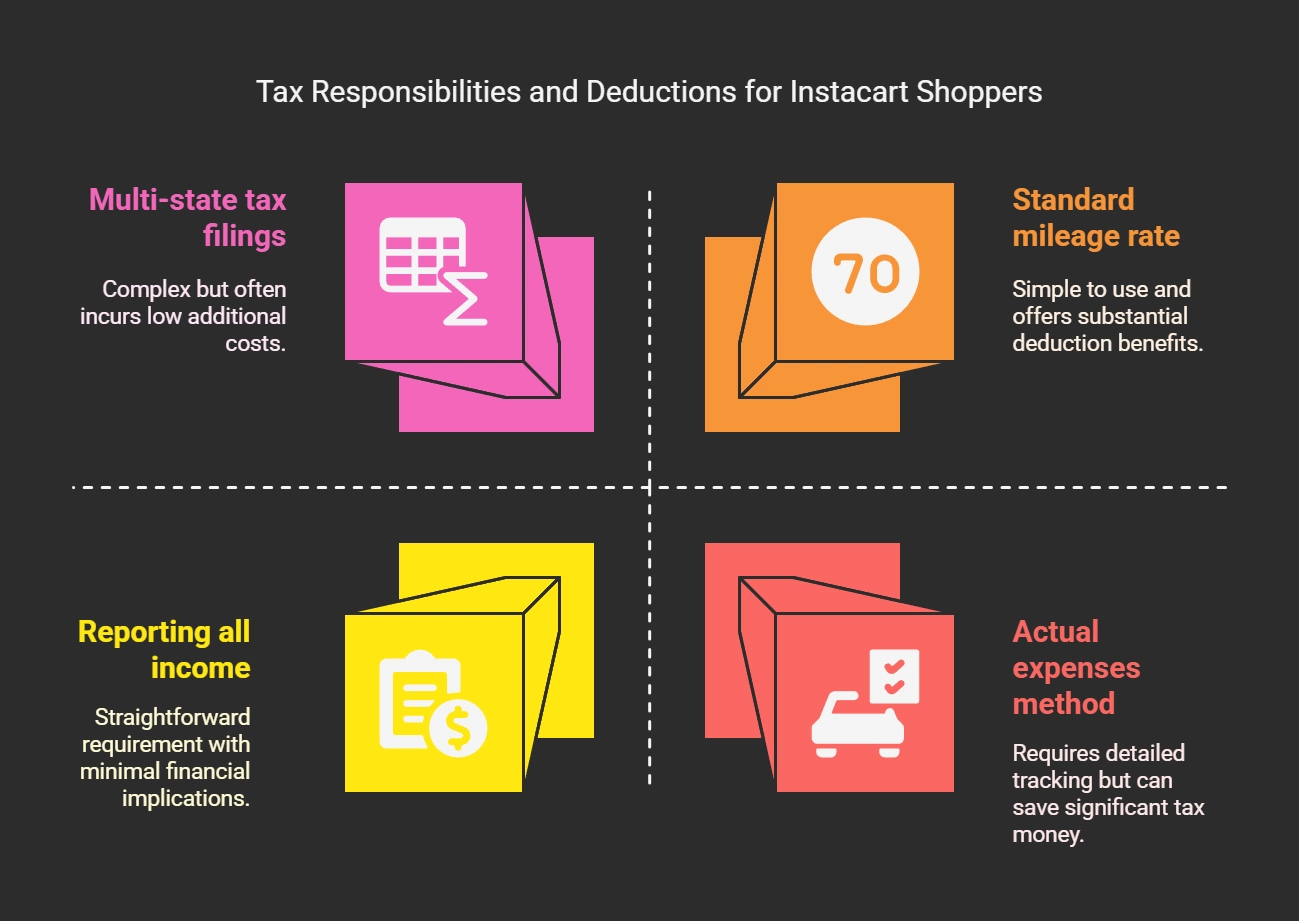
1099 Tax Deductions
One of the biggest advantages of earning 1099 income is the ability to deduct business expenses, significantly lowering your taxable income.
Common Deductions for 1099 Workers
- Home Office Deduction: Deduct a portion of rent, utilities, and repairs for a space used exclusively for work.
- Mileage and Travel: Deduct the standard mileage rate (70 cents per mile in 2025) or actual vehicle expenses.
- Supplies and Equipment: Deduct items like computers, software, and tools used for business.
- Health Insurance Premiums: Deduct premiums for yourself, your spouse, and dependents.
Filing for Deductions
- Use Schedule C (Profit or Loss from Business) to report your deductions.
- Keep detailed records of receipts, invoices, and mileage logs.
- File your taxes by the annual deadline (April 15).
Tax Credits and State-Specific Considerations
Navigating tax credits and state-specific tax obligations is a critical step in minimizing your overall tax liability as a 1099 earner. While tax deductions lower your taxable income, tax credits directly reduce the amount of taxes you owe, offering significant savings. Additionally, state tax rules can vary widely, and understanding them ensures compliance and helps you avoid surprises at tax time.
Tax Credits for 1099 Earners
As a self-employed individual, you may qualify for several tax credits that directly lower your tax bill. These include:
- Saver’s Credit: For contributions to retirement accounts like SEP-IRAs or Solo 401(k)s.
- Premium Tax Credit: For health insurance purchased through the marketplace.
- Education Credits: Like the Lifetime Learning Credit for skill-building courses.
State-Specific Tax Obligations
In addition to federal taxes, many states require 1099 earners to pay state income tax on their net earnings. However, tax rules and requirements differ by state, so it’s essential to stay informed:
- Research your state’s income tax rules.
- If you work in multiple states, allocate income and pay taxes in each state as required.
Common Mistakes and Best Practices
Managing taxes as a 1099 earner can be complex, and even small errors can lead to audits, penalties, or missed savings. By understanding common mistakes, what triggers IRS audits, and adopting best practices, you can confidently handle your tax obligations while staying compliant.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Missing quarterly tax payments.
- Overstating or misreporting deductions.
- Failing to maintain accurate records.
- Not reporting all income.
Best Practices
- Separate personal and business finances.
- Stay informed about tax law updates.
- Use tools like MileageWise to track mileage and expenses automatically.
Tax Planning for the Future
Effective tax planning goes beyond filing your annual return—it’s about creating strategies that help you minimize your tax burden and achieve long-term financial stability. As a 1099 earner, proactive tax planning is crucial to managing variable income, maximizing savings, and preparing for the future.
Long-Term Strategies
- Set Up Retirement Accounts: SEP-IRAs, Solo 401(k)s, and Traditional IRAs reduce taxable income while building your future savings.
- Build a Tax Savings Fund: Save at least 25-30% of your earnings for taxes.
Seek Professional Advice
Consulting a CPA or tax planner can help you develop customized strategies, navigate complex tax rules, and prepare for audits.
Leveraging MileageWise for Tax Savings
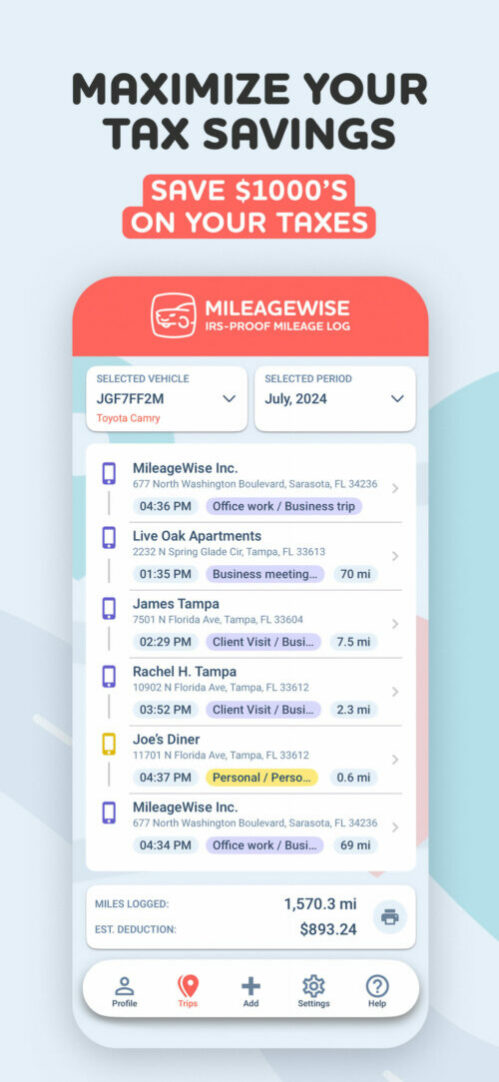
For 1099 earners, maximizing mileage deductions is one of the most effective ways to lower taxable income. MileageWise is designed to make this process seamless, accurate, and stress-free. From tracking mileage automatically to generating IRS-proof logs, this tool is a game-changer for freelancers, independent contractors, and gig workers.
How MileageWise Mileage Tracker Simplifies Tax Preparation
MileageWise is not just a tool; it’s your co-pilot in the realm of 1099 taxes, designed to meticulously track, log, and optimize your 1099 mileage deductions. Here’s how it revs up your tax-saving engine:
- Automatic Mileage Tracking: Tracks every trip with precision.
- IRS-Proof Logs: Generates compliant reports for deductions.
- AI-assisted Trip Recovery: Reconstructs logs for missed trips.
Key Takeaways
Handling 1099 taxes doesn’t have to be stressful. By understanding your tax obligations, leveraging tools like MileageWise, and staying proactive with planning, you can save money, avoid penalties, and simplify tax season.
Level Up Your Mileage Tracking
MileageWise: Tracks trips automatically via vehicle movement, Bluetooth, and Plug’N’Go without draining your battery.
AI-Powered Mileage Log Generator: Our AI tool helps reconstruct past mileage logs and fill gaps in your log to ensure compliance.
Built-in IRS Auditor: Checks and corrects up to 70 potential red flags in logs, ensuring they meet IRS standards for tax deductions.
Web Dashboard & Team Collaboration: Manage logs, import trips, and collaborate with teams through the web dashboard, ideal for businesses.
Try it for free for 14 days. No credit card required!
FAQ
What if I overestimate or underestimate my earnings?
If you overestimate, you can adjust your next payment. If you underestimate, you may owe more at tax time, possibly with penalties. It’s crucial to revisit your estimates each quarter and adjust as needed.
How do I make estimated tax payments?
Payments can be made online through the IRS website, by phone, or by mail with a check or money order using the 1040-ES payment voucher.
What should I do if I receive an audit notice?
Don’t panic. Review the notice to understand what the IRS is questioning. Gather all relevant documents and consider consulting with a tax professional for guidance.
How much should I save for taxes?
A common rule of thumb for 1099 earners is to set aside 30-35% of your income for taxes. Using a 1099 tax calculator with deductions can help you estimate more accurately based on your specific situation.
Can I deduct my meals and entertainment?
Meals can be deductible if they are directly related to your business and necessary. Entertainment expenses, however, are no longer deductible as of the last update.
Does 1099 take out taxes?
No, taxes are not automatically withheld from payments reported on a 1099 form; you are responsible for paying estimated taxes quarterly.
How to file taxes with 1099?
To file taxes with a 1099 form, report your total income from all 1099 forms on Schedule C of your tax return, calculate deductions, and include this in your Form 1040.
How do I calculate taxes on 1099 income?
Utilize a tax calculator with a 1099 feature to estimate your tax liability. Input your total income from 1099s, and don’t forget to subtract any deductible expenses.
What can I deduct as a 1099 employee?
Absolutely! Deductions like home office expenses, supplies, and mileage can significantly reduce your taxable income. Make sure to keep detailed records of all your business-related expenses.
When are estimated tax payments due?
Estimated tax payments are due four times a year: April 15, June 15, September 15, and January 15 (of the following year).