April 29, 2025
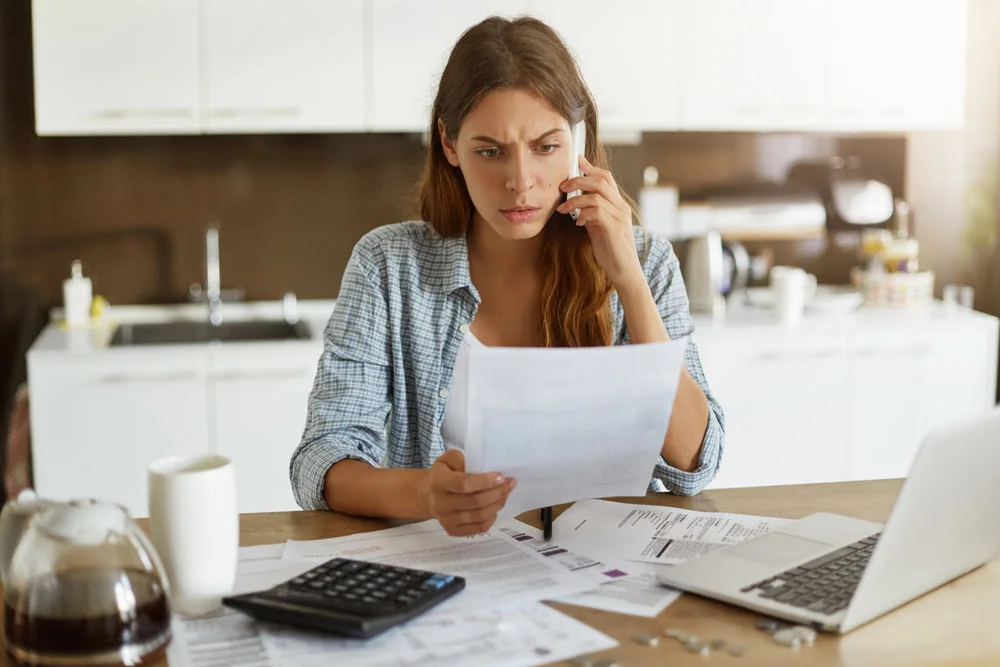
Are you a freelancer or independent contractor? Do you get paid with a 1099 form? Then you need a 1099 tax calculator! This tool helps you figure out how much tax you owe. It saves you time and helps you avoid surprises from the IRS. Read on to learn how it works.
1099 Tax Calculator (2025)
Table of Contents
How Does a 1099 Tax Calculator Work?
A 1099 tax calculator figures out your taxes differently than for someone with a W-2 form. With a W-2, your employer takes out taxes before you get paid. With a 1099, you get paid the full amount, and you have to figure out and pay your own taxes. This includes federal income tax, and importantly, self-employment tax. The calculator takes your income, your state, and your deductions to give you an estimate.
It’s important to understand the self-employment tax. The IRS has a tax rate of 15.3% for self-employment. This covers Social Security and Medicare taxes. The federal income tax rate however depends on your income. You can see which federal income tax bracket applies to you.
For many 1099 workers, the amount they should set aside for taxes is usually between 20% and 35% of their income. But this can change based on your income and deductions. A good calculator helps you figure out what percentage is right for you. You can also watch this video from CountyOffice.org to learn more about how to calculate federal income tax for 1099 income: How To Calculate Federal Income Tax For 1099?
Why Use a 1099 Tax Calculator?
Using a 1099 tax calculator has big benefits. For starters, it gives you accurate tax estimates. This is key for paying estimated taxes each quarter. If you don’t pay enough throughout the year, the IRS can charge you a penalty. The calculator helps you avoid this.
It also saves you a lot of time. Instead of crunching numbers yourself, the calculator does the hard work. This frees you up to focus on your business. Plus, a calculator helps you plan your money better. When you know how much to set aside for taxes, you won’t be caught off guard during tax season. This gives you more peace of mind. One user mentioned that using a calculator helped them feel “more in control of their finances.”
Paying Estimated Quarterly Taxes
As a 1099 worker, you usually need to pay taxes throughout the year, not just in April. These are called estimated quarterly taxes. The 1099 tax calculator helps you figure out how much you should pay each quarter.
Paying estimated taxes helps you avoid penalties from the IRS. The deadlines for quarterly payments are:
- April 15th
- June 15th
- September 15th
- January 15th of the following year
Make sure you pay on time! The IRS has more resources on self-employment taxes here.
How to Use Your 1099 Tax Calculator
Using a 1099 tax calculator is usually pretty simple. Here are the basic steps:
- Enter Your Income: Put in your total income from your 1099 forms.
- Select Your State: If your state has additional tax, enter the amount in the calculator
- Add Your Deductions: This is where you can save money! Enter your business expenses that you can deduct.
- See Your Estimate: The calculator will give you an estimated tax amount.
Understanding Deductions and Your 1099 Tax Calculator
Deductions are crucial for 1099 workers. They lower your taxable income, which means you pay less tax. A good 1099 tax calculator should help you factor in common deductions.
Here are some common deductions for self-employed people:
- Mileage: You can deduct the cost of using your car for business. Tracking your mileage is very important!
- Home Office: If you use part of your home regularly and exclusively for business, you can deduct expenses related to that space.
- Supplies: Things you buy to run your business, like a new computer or paper clips.
- Business Travel: Costs for business trips.
- Health Insurance Premiums: If you pay for your own health insurance and don’t have access to employer-sponsored health insurance, you might be able to deduct your premiums.
- Qualified Business Income (QBI) Deduction: This deduction allows eligible self-employed individuals to deduct up to 20% of their qualified business income.
Tracking your expenses throughout the year is key to taking advantage of deductions. Consider using digital tools like apps or spreadsheets to keep good records. This makes using a 1099 tax calculator much more effective.
Why Mileage Tracking is Your Secret Weapon for 1099 Taxes
Tracking your miles when you’re self-employed is super important. The 1099 mileage deduction is often the biggest source of tax savings for self-employed earners. The IRS has clear rules about keeping detailed records for your business miles. If you don’t track your miles correctly, you could miss out on thousands of dollars you could have taken as a deduction. Think about how much money you drive for work! That adds up fast. Accurate mileage logs mean you can deduct more from your taxable income, which means a lower tax bill. It’s a direct way to save money when you’re self-employed.
The MileageWise Difference: Smart Tech for Your Miles
This is where MileageWise really helps you with your 1099 tax. We have unique technology that makes tracking and logging miles simpler and much more accurate than other methods.
The MileageWise Mobile App
Our app is designed for real-time tracking. It’s automatic, so you don’t have to remember to start and stop it. It can track using different methods like watching for vehicle movement, when your phone is charging, or even by connecting to Bluetooth in your car.
- It doesn’t drain your phone battery like some other apps.
- There are no annoying ads.
- It uses very little mobile data.
- Most importantly, we care about your privacy. We don’t share your data.
This app automatically logs your trips and separates business trips from personal ones.
The MileageWise Web Dashboard
Sometimes you forget to track a trip, or maybe you’re trying to catch up on past miles. Our web dashboard is packed with tools to handle that.
- Google Maps Timeline Integration: This is totally unique to MileageWise. You can import your location history from Google Maps directly into MileageWise. This is a game-changer for recreating past trips quickly and accurately. It puts us miles ahead of other apps.
- AI Wizard Mileage Log Generator: This is another exclusive tool. If you have gaps in your records, this AI helps fill them in by intelligently suggesting trips based on patterns, while making sure everything meets IRS rules. You don’t have to guess or try to remember dozens of trips.
- Comprehensive Trip Management: You can easily review, edit, and categorize your trips on the web dashboard.
- Built-in IRS Auditor: This amazing tool automatically checks your log for 70 common mistakes or “red flags” that the IRS looks for during an audit. It helps you fix issues before you file, giving you peace of mind that your log is audit-proof.
Customer Story: From Stress to Savings
“I used to dread tax time. As a freelance graphic designer, all my income came from different clients, and I’d get a pile of 1099 forms in January. Trying to figure out my taxes was a nightmare. I’d spend hours with spreadsheets, guessing how much to set aside, always worried I was forgetting something or making a mistake. I knew I wasn’t tracking my mileage right, and I felt like I was missing out on deductions.
Then I heard about MileageWise. At first, I was skeptical. I mean, could an app really make taxes easier? I thought it would be too complicated or too expensive for a freelancer like me. I also had a ton of old trips I hadn’t logged, and I didn’t think anything could help me with that.
But I learned about their AI Wizard Mileage Log Generator and Google Maps Timeline integration. I decided to give it a try. It was simpler than I thought. I imported my Google data, and the AI Wizard worked its magic. Suddenly, I had potential mileage deductions I didn’t even know existed. Because I used MileageWise, I could confidently use a 1099 tax calculator with accurate mileage data. I saved thousands more on my taxes than I expected! Tax season is still work, but it’s not a stressful nightmare anymore.”
Try MileageWise for free for 14 days. No credit card required!
AI Logs & Google Timeline Import
Conclusion: Take Control of Your 1099 Taxes
If you receive 1099 income, using a 1099 tax calculator is essential. It helps you understand how much tax you owe, find deductions, and pay your estimated quarterly taxes on time. This saves you money, time, and stress.
Here are the steps you should take:
- Find a trusted and up-to-date 1099 tax calculator.
- Gather your income information from your 1099 forms.
- Track your business expenses throughout the year, especially your mileage. Consider a tool like MileageWise to make this easy and audit proof.
- Use the calculator to estimate your taxes and quarterly payments.
- Set aside the estimated tax amount from each payment you receive.
- Pay your estimated quarterly taxes by the deadlines.
By taking these steps, you can take control of your 1099 taxes and feel confident during tax season.
FAQ
What is a 1099 tax calculator?
A 1099 tax calculator is an online tool that estimates how much federal (and sometimes state) tax you owe based on income earned as an independent contractor or freelancer. It helps determine your income tax and self-employment tax liability after accounting for deductible expenses.
How do I estimate my self-employment taxes on 1099 income?
To estimate self-employment taxes, a 1099 calculator typically applies the 15.3% self-employment tax rate (12.4% for Social Security and 2.9% for Medicare) to your net earnings. Your net earnings are your total 1099 income minus any qualified business expenses.
What information do I need to use estimate my 1099 taxes?
You should have the following:
– Total 1099 income
– Estimated deductible business expenses (e.g. office supplies, software)
– State of residence (some tools include state taxes)
| MileageWise | Other Mileage Tracker Apps | Other GPS Based Trackers | Excel | Tax Professional | |
| Mobile App for Ongoing Tracking | |||||
| Web Dashboard to Manage Trips | |||||
| Imports Trips and Locations from Google Timeline | |||||
| Lifetime Deals Available | |||||
| Average Reported Business Mileage Deduction | $12,000 | $710-$8500 | $400-$5,700 | $200-$2,000 | |
| Average Time Creating Retrospective Mileage Log (Yearly) | 7 minutes | 180 minutes | 180 minutes | 180 minutes | N/A |
| AI Wizard Mileage Log Generator for Retroactive Mileage Recovery | |||||
| Produces IRS-Proof Mileage Logs | |||||
| Free Phone Support with Live Agent | |||||
| Mileage Log Preparation Service | |||||
| Data Accessible in the Cloud |