Last updated on October 3, 2024
As the gig economy is expanding globally, the United States is no exception either. More than one-third of the population, about 59 million people are working in the gig business, looking to make money independently. Another interesting fact is that more than 90% of Americans would consider freelancing or independent contracting work. It’s no surprise, there are tons of side hustle opportunities for gig workers.
However, managing taxes as a gig worker is vastly different from traditional employment. In this blog, we’ll explore gig worker tax deductions, how to manage your taxes as an independent contractor, and what expenses you can deduct to lower your 1099 tax burden.

Table of Contents
What is Gig Work?
Gig work refers to short-term or freelance jobs where individuals act as independent contractors. Unlike traditional employment, gig workers don’t have taxes withheld from their paychecks. Instead, they are responsible for managing their own tax payments, making it essential to understand the rules around gig worker tax deductions.
How do I Manage Taxes as a Gig Worker?
Managing taxes can feel overwhelming for gig workers, but breaking it down into simple steps can make it easier.
1. Track Expenses and Maintain Records
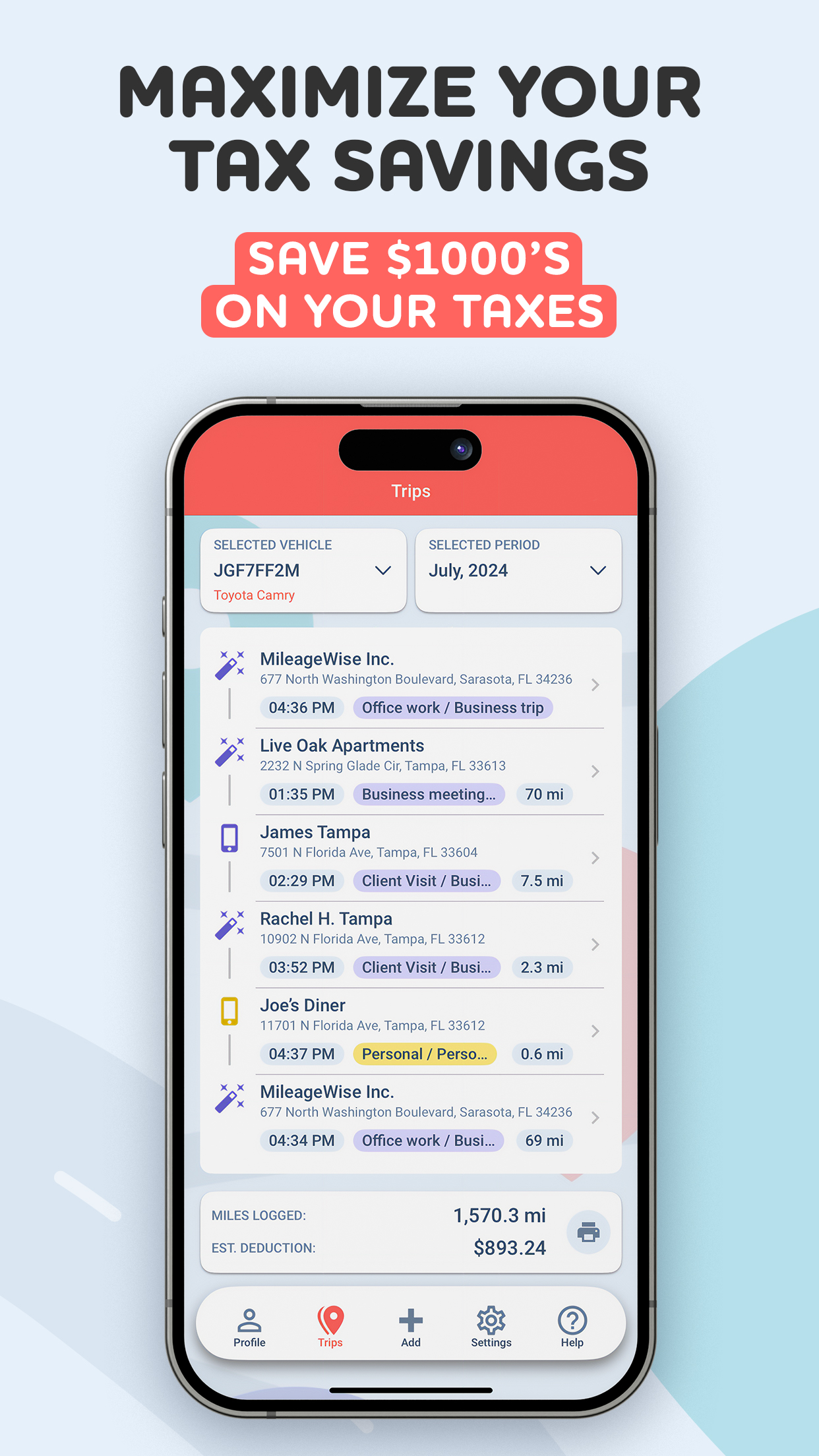
To calculate gig worker tax deductions, it’s important to track all business-related expenses. Keep receipts, invoices, and records of any purchases you make related to your side gig work. Furthermore, keep a detailed mileage log to claim mileage deductions.
Download MileageWise’s automatic mileage tracker app from Google Play or the App Store & try it for free for 14 days. No credit card required!
2. Pay Estimated Taxes
As a gig worker, you must pay estimated taxes quarterly. This ensures you’re not hit with a large tax bill when you file your tax return.
3. Prepare to File Your Taxes
Before filing, organize all your records, including any income and expenses from your gig, and any tax forms. This will make the process smoother and help maximize your gig worker tax deductions.
4. File Your Tax Return
When filing your taxes, you’ll need to fill out several tax forms, such as the IRS Form 1040, and attach a Schedule C to report income and expenses. This is where you’ll claim your tax reimbursements.
Am I Eligible for Tax Credits?
In addition to deductions, some gig workers may qualify for tax credits, such as the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) which can further reduceyour tax liability.
What Expenses Are Tax Deductible?
There are many expenses you can deduct as a gig worker to lower your tax bill. Let’s break down the most common ones:
1. Cell Phone Bill
If you use your phone for gig work, you can deduct a portion of your cell phone bill. Be sure to calculate the percentage of time it’s used for business versus personal use.
2. Technology Expenses
Any technology-related expenses, such as software subscriptions or computer purchases, can qualify as gig worker tax deductions. Keep detailed records of these expenses.
3. Home Office Expenses
If you have a dedicated space in your home for gig work, you can claim a home office deduction. Make sure the space is used exclusively for business.
4. Supplies and Equipment
Any supplies or equipment you purchase for your gig work are eligible for gig worker tax deductions. Whether it’s office supplies or special tools, keep those receipts.
5. Equipment Depreciation
Larger equipment, such as computers may qualify for depreciation deductions. You can claim a portion of the cost each year.
6. Health Insurance Premiums
As a self-employed gig worker, you may deduct health insurance premiums for yourself and your family.
7. Vehicle Expenses
Many gig workers use their personal vehicle for business. Whether you’re driving for a rideshare company or delivering food, you can deduct vehicle-related expenses.
Mileage Deduction
For gig workers who drive often, mileage deduction is a key component of tax savings. This is because vehicle expenses can add up quickly. You can either use the standard mileage rate or track actual expenses, such as gas and maintenance, to calculate this deduction.
Note, that accurate record-keeping is key to maximizing your mileage deduction. Here is the best mileage tracker app for the task.
Keeping Records for Mileage Deduction
You have two main options when it comes to tracking vehicle expenses and mileage:
Vehicle Expense Log
This method involves recording every vehicle-related expense you incur throughout the year, including fuel, insurance, maintenance, and repairs. At tax time, you’ll total these expenses and calculate the percentage used for business. This can be a bit more complex, as you need to separate personal use from business use.
Mileage Log
The simpler option for many gig workers is to track the number of miles you drive for business purposes. The IRS provides a standard mileage rate each year, which you can use to calculate your deduction. All you need to do is multiply your business miles by the standard rate to get your deduction amount.
Manual Tracking vs. Digital Tracking
When it comes to keeping these logs, you have two main choices: manual tracking or using a digital solution.
Manual Tracking
Manual tracking involves writing down your miles or vehicle expenses in a notebook or entering them into a spreadsheet. While this method can work, it’s time-consuming, prone to errors, and easy to forget. You must remember to log every trip and expense consistently.
Digital Tracking
Digital tools like apps can make tracking mileage and expenses much easier. Apps like MileageWise allow you to automatically track your trips, calculate mileage deductions, and store all your records in one place. The app can even help you recover missed trips by creating a mileage log based on your past drives, which is especially useful if you forget to track some trips manually.
Digital tracking is more accurate, saves time, and helps ensure you don’t miss any valuable deductions. Plus, it simplifies tax preparation since all your records are stored neatly in one place.
MileageWise: The Best MileageTracker App for Gig Workers
Gig workers benefit greatly from using MileageWise because it simplifies the often complicated process of tracking and reporting mileage, which is crucial for maximizing tax deductions and staying compliant with IRS standards. Special features for gig workers include:
Time-Saving Features
Automatic mileage log creation and mileage tracking saves you a whole lot of time that you can instead invest in your gig. Also, the software offers easy integration with other platforms, simplifying the process of trip import and organizing your invoices.
Customizable Tracking
The app only tracks your points of arrival to protect your privacy and mobile data. You have the option to manually enter your arrival or choose an automatic tracking mode that suits you best. If you choose an automatic method, the app notices if you have stopped for at least ten minutes by default or got out of the vehicle. However, if your phone usually does not exit the vehicle – like in the case of rideshare drivers – the Standby Timer Feature allows you to set the time you have to stay idle in order for the app to record your arrival. No more missed entries or recording stops at a red light!
And Many more:
Level Up Your Mileage Tracking
Automatic Tracking: Tracks trips automatically via vehicle movement, Bluetooth, and Plug’N’Go without draining your battery.
AI-Powered Mileage Recovery: The AI Wizard helps reconstruct past mileage logs, filling gaps in your log to ensure compliance.
Built-in IRS Auditor: Checks and corrects up to 70 logical errors in logs, ensuring they meet IRS standards for tax deductions.
Web Dashboard: Manage logs and import trips through the web dashboard.
Download MileageWise’s automatic mileage tracker app from Google Play or the App Store & try it for free for 14 days. No credit card required!
Conclusion
Navigating gig worker taxes doesn’t have to be stressful. By understanding the deductions available to you and staying organized throughout the year, you can lower your tax bill and avoid surprises. Use this guide to manage your taxes, claim your gig worker tax deductions, and ensure you’re making the most of your hard-earned income.
FAQs
What is the gig work, and how does it impact my taxes?
The gig economy is about flexible, temporary work, unlike traditional jobs. As a gig worker, you’re seen as self-employed for taxes. This means you pay self-employment tax and income tax on your earnings. It’s important to plan your taxes well to avoid penalties and get the most deductions.
What are some common tax deductions for gig workers?
Gig workers can deduct many business expenses on their taxes. These include car costs, home office expenses, and equipment. You can also deduct legal fees, advertising, and more. Keeping good records and receipts is key to claiming these deductions.
How do I determine if I qualify for the home office deduction?
You need a dedicated space for your gig work to qualify for the home office deduction. This space must be used only for work and not for personal use. You can then deduct a part of your home expenses based on the space’s size.
Should I deduct my actual vehicle expenses or use the standard mileage rate?
The choice depends on your situation. The standard mileage rate is simpler but might not give you the biggest deduction. The actual expense method requires more records but could save more, especially with expensive vehicles. Think about your business miles, vehicle costs, and recordkeeping ease to decide.
How do I handle self-employment tax and estimated tax payments?
You must pay self-employment tax for Social Security and Medicare. You also need to make estimated tax payments if you owe more than $1,000 on your taxes. A tax professional or software like TurboTax can help you meet these requirements and make accurate payments.
| MileageWise | Other Mileage Tracker Apps | Other GPS Based Trackers | Excel | Tax Professional | |
| Mobile App for Ongoing Tracking | |||||
| Web Dashboard to Manage Trips | |||||
| Imports Trips and Locations from Google Timeline | |||||
| Lifetime Deals Available | |||||
| Average Reported Business Mileage Deduction | $12,000 | $710-$8500 | $400-$5,700 | $200-$2,000 | |
| Average Time Creating Retrospective Mileage Log (Yearly) | 7 minutes | 180 minutes | 180 minutes | 180 minutes | N/A |
| AI Wizard Mileage Log Generator for Retroactive Mileage Recovery | |||||
| Produces IRS-Proof Mileage Logs | |||||
| Free Phone Support with Live Agent | |||||
| Mileage Log Preparation Service | |||||
| Data Accessible in the Cloud |








