When you get a 1099 form, you might ask, is 1099 taxable income? Yes, it usually is, but there are some details to know. We’ll cover everything about 1099 income, its tax impact, and how to follow IRS rules.

Level Up Your Mileage Tracking
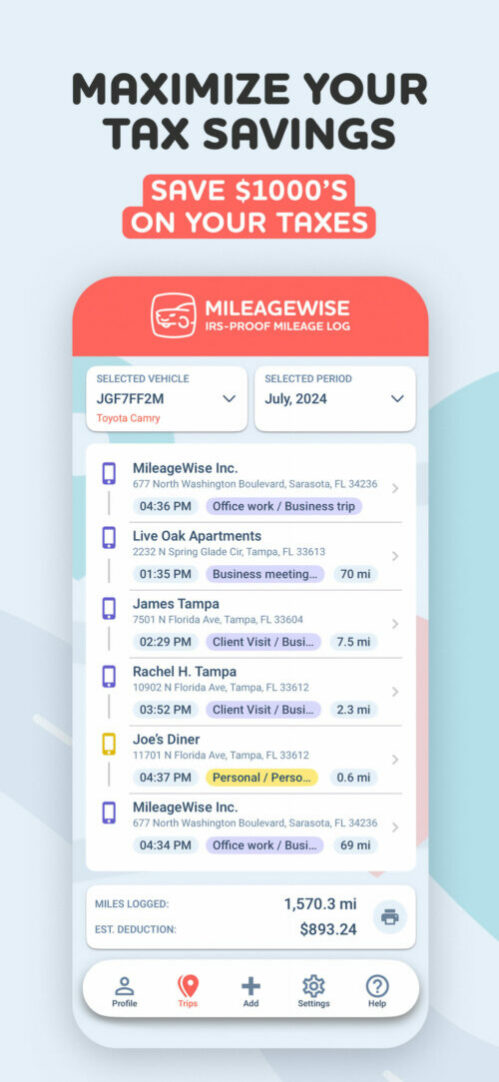
MileageWise: Tracks trips automatically via vehicle movement, Bluetooth, and Plug’N’Go without draining your battery.
AI-Powered Mileage Recovery: The AI Wizard helps reconstruct past mileage logs, filling gaps in your log to ensure compliance.
Built-in IRS Auditor: Checks and corrects up to 70 logical errors in logs, ensuring they meet IRS standards for tax deductions.
Web Dashboard & Team Collaboration: Manage logs, import trips, and collaborate with teams through the web dashboard, ideal for businesses.
Try it for free for 14 days. No credit card required!
What is a 1099 Form?
The 1099 form is an IRS document for income not from a job. Unlike W-2s for employees, 1099s are for freelancers and others. Here are some common types:
- 1099-MISC: Reports miscellaneous income.
- 1099-NEC: For non-employee compensation.
- 1099-INT: Interest from banks or financial institutions.
- 1099-DIV: Dividends and distributions.
Is 1099 Income Taxable?
So, is 1099 taxable income? Yes, most 1099 income is taxable by the IRS. You must report it on your tax return, even without a 1099 form. Here are important points:
Types of 1099 Income
Different 1099 incomes have different tax rules:
- Self-Employment Income: Freelance or contractor work on 1099-MISC or 1099-NEC is taxed. You pay self-employment and regular income tax.
- Interest and Dividend Income: Income on 1099-INT or 1099-DIV is taxable. Include it in your yearly income.
- Rental Income: Rental income on a 1099 is taxed as income.
How Taxation Works for 1099 Income
Understanding IRS rules for 1099 income is key. Here’s a simple guide:
- Self-Employment Tax: If you make over $400 a year from self-employment, you pay self-employment tax plus regular income tax.
- Tax Deductions: As self-employed, you can deduct work-related expenses. This lowers your taxable income. Common deductions include:
- Home office expenses
- Business travel costs
- Supplies and materials
- Estimated Taxes: Unlike employees, you might need to pay estimated taxes throughout the year.
If you need a more precise estimation visit our 1099 tax calculator.
Filing Your Taxes with 1099 Income
When filing taxes, follow these steps for 1099 income:
- Gather Your 1099 Forms: Collect all 1099 forms you got during the year.
- Report Your Income: Use your 1099s to report income on your tax return. For self-employment, use Schedule C (Form 1040).
- Calculate Deductions: Deduct business expenses on Schedule C to lower your taxable income.
- Pay Any Taxes Owed: If you owe taxes from 1099 income, pay it to avoid penalties.
Common Questions about 1099 Taxable Income
Many people have questions about 1099 taxes. Here are some answers.
Do I have to pay taxes on 1099 income if I didn’t receive a 1099 form?
Yes, you must report all income, including 1099 income, even without a 1099 form. Keep detailed records of your income to report it right.
What if I believe my 1099 form is incorrect?
If you think your 1099 form has mistakes, reach out to the issuer for a fix. Always report your income based on your records.
Can I deduct expenses for my 1099 income?
Yes, you can deduct business expenses related to your 1099 work. Keep receipts and detailed records to back up your deductions.
Conclusion
In summary, the answer to is 1099 taxable income? is a clear yes. Whether you’re a freelancer, independent contractor, or have other income sources, knowing your tax duties is key. By keeping accurate records, reporting income correctly, and using deductions, you can handle 1099 income well. Always get advice from a tax expert for personalized help and to follow IRS rules.


