IRS Mileage Guide
Home » Mileage Tax Deduction
Last Updated: July 21, 2025
The self-employed mileage tax deduction is a big win for anyone using their car for work, charity, or medical needs. It helps you save money by lowering your taxable income. The IRS updates these rates every year, so staying current is key for self-employed professionals, freelancers, and small business owners.
Table of Contents
Understand Your Mileage Tax Deduction Eligibility and Rates
Knowing if and how you qualify for the mileage tax deduction is your first step. Let’s break down who can claim it and what the latest rates are for 2025.
Who Can Claim the Mileage Tax Deduction?
If you use your vehicle for specific activities, you might be eligible! This deduction primarily benefits those who are:
- Self-Employed Individuals: If you’re a freelancer, 1099 contractor, gig economy driver, or run your own business, you are eligible for a self-employed mileage deduction on your business miles.
- Volunteers: Miles driven for charitable organizations are deductible.
- Individuals with Medical Needs: If you drive for medical appointments or treatments, those miles can be deducted.
- Moving for Work: Certain moving expenses, including mileage, can be deducted if you’re relocating for a new job. (Note: This is often for active military personnel post-2018 tax law changes).
IRS Standard Mileage Rates Overview
The IRS adjusts these rates annually to reflect changes in vehicle operating costs like fuel and maintenance. Here’s a quick look at the rates you need to know:
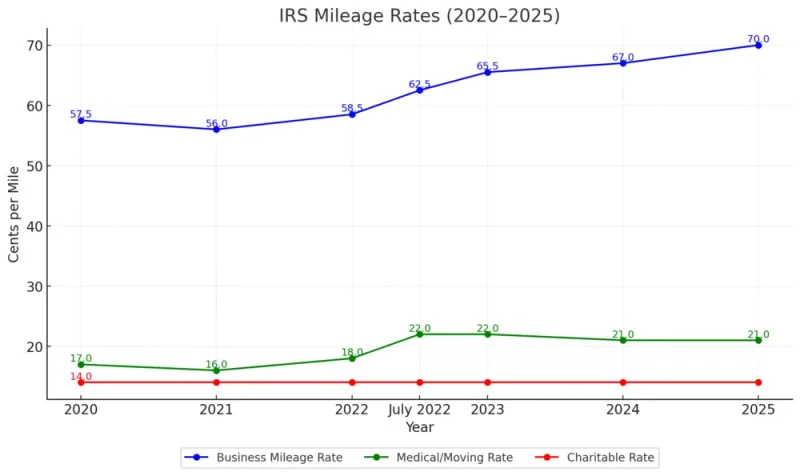
The increase to $0.70 per mile for business in 2025 is the highest in recent years. This is great news, as an increased IRS mileage rate enables larger reimbursements for people hitting the road for work. For example, a food delivery driver averaging 200 miles a week for business could save up to $7,000 in 1099 mileage deductions. This shows how crucial it is to track every mile!
Watch this video for more insights: What Mileage Is Tax Deductible?
How to Calculate Your Mileage Deduction
Once you know you’re eligible, the next step is figuring out how to calculate your mileage tax deduction. You have two main ways to do this: the standard mileage rate method or the actual expense method.
- Standard Mileage Rate Method: This is often the simpler choice. You just multiply your total eligible business miles by the IRS’s standard rate for that year.
- Actual Expense Method: With this method, you track and deduct all your vehicle-related costs that are directly tied to your business use.
For a deeper dive into IRS rules for mileage reimbursement, check out this helpful IRS resource: Topic no. 510, Business Use of Car.
Record-Keeping Rules for IRS Mileage Reimbursement
No matter which method you choose, excellent record-keeping is non-negotiable. The IRS demands a detailed, contemporaneous mileage log. This isn’t just a suggestion; it’s a major audit trigger if your records are incomplete.
What should your mileage log include?
- Date of the Trip: When did the trip happen?
- Starting and Ending Location: Where did you start and end?
- Purpose of the Trip: Why were you driving (e.g., client meeting, supply run, delivery)?
- Total Miles Driven: The calculated distance for that trip.
- Starting and Ending Odometer Readings of the Year: Essential for justifying your miles.
Remember, the IRS takes mileage logs very seriously. If you’re audited, even a small mistake can result in the disallowance of your deduction. This is where smart tools come in!
MileageWise: Your Partner in Maximizing Your Mileage Tax Deduction
At MileageWise, we understand the complexities of mileage tracking and the importance of an audit-proof mileage tax deduction. Our solutions are built to simplify your life, ensure compliance, and maximize your savings. We are seasoned experts in IRS compliance, focusing on U.S.-based self-employed professionals, small business owners, and gig economy workers.
Mobile App for Tracking Miles
- Auto-Tracking Your Drives: Choose from multiple modes and let the app capture drives for you.
- Easy Onboarding: Get started fast, so you can focus on claiming mileage deductions instead of figuring out a complicated system.
- No Ads, Full Privacy: Track your mileage without interruptions or data-sharing concerns.
- Reliable Backup Detection: Accurately identifies where trips began, solving a common problem in other trackers.
- Customizable Route Logging: Choose exact routes or let the app calculate optimized distances.
- Waze Integration: Navigate with Waze while MileageWise tracks trips in the background.
- Expense Logging Add-on: Keep both your mileage and business expenses together for streamlined tax reporting.
Dashboard for a Retrospective Mileage Log
- Google Maps Timeline Sync: Forgot to track a drive? Have you gone months or years without tracking? Import your Google Location History to recover missed trips and still claim your deduction.
- AI-Powered Mileage Wizard: Quickly rebuild unlogged past drives with AI -no more guesswork.
- IRS-Proof Mileage Auditor: Get peace of mind knowing your logs follow IRS standards. Beyond applying rules, your logs are also scanned for any inconsistencies that might trigger an audit.
- Bulk Import Options: Add clients or routes in bulk — great for anyone with repeat destinations, high trip volume, or anyone who wants to switch from a spreadsheet to an automatic solution.
- Full Trip Control: Organize recurring drives, categorize trips, and make batch edits — ideal for maximizing deductions with minimal effort.
Lifetime Plans That Maximize Mileage Deduction Value
Say goodbye to ongoing subscription fees. MileageWise is the only mileage tracker offering lifetime access — helping you deduct more while paying less in the long run.
- Small Lifetime Deal: Log unlimited miles and create deduction-ready mileage reports with AI assistance — all for a one-time fee of $119. A simple, budget-friendly solution for consistent tax savings.
- Gold Lifetime Plan: Access all features, including retroactive trip recovery, Google Timeline import, and IRS-compliant reports. Perfect if you need logs for previous tax years or want to stay fully prepared for audits.
Support That Understands Mileage Deduction Deadlines
Whether you’re logging trips before tax season or rebuilding past mileage, our team is here to help — fast. We know time is money, especially when you’re chasing down on the 1099 mileage deduction. Count on responsive, expert support whenever you need it — no waiting, no frustration.
Try MileageWise for free for 14 days. No credit card required!
Customer Story: Stress-Free Deductions with MileageWise
As a freelance caterer, I drive a lot for consultations, supplies, and events, but I tracked mileage in a messy notebook. I’d forget odometer readings, mix up trip purposes, and scramble to make sense of it all before the tax deadline. My accountant once said I was likely missing out on thousands in deductions.
That’s when I tried MileageWise. Setup was easy, and the biggest win? Their AI-Powered Mileage Wizard helped me reconstruct an entire quarter of missed trips wit the help of my Google Location History. For the first time, I filed with confidence, claimed a larger mileage tax deduction, and had a fully audit-proof log. It turned a major stress point into a smooth process.
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Mileage Deduction
Maximizing your mileage tax deduction is not just about saving money; it’s about smart financial management and peace of mind.
Here are your actionable steps:
- Know the Rates: Stay updated on the latest IRS standard mileage rates.
- Choose Your Method Wisely: Decide whether the standard mileage rate or actual expense method is best for your situation.
- Track Diligently: Keep detailed, contemporaneous records of all your business, medical, or charitable miles.
- Embrace Technology: Use mileage tracking apps like MileageWise to automate and simplify your logging.
- Audit-Proof Your Records: Ensure your logs are IRS-compliant to avoid potential issues.
- Seek Expert Help: If in doubt, consult a tax professional.
FAQ
Who is eligible to claim the mileage tax deduction?
Self-employed individuals, 1099 workers, and business owners can claim a self-employed mileage deduction for business-related driving. Employees cannot deduct unreimbursed work mileage due to changes from the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (effective 2018-2025). Exceptions exist for certain Armed Forces reservists, qualified performing artists, and some government officials.
What kinds of driving are eligible for the business mileage deduction?
Eligible business miles include:
- Driving between work sites (not your main place of business)
- Visiting clients/customers
- Traveling to meetings, conferences, or job sites
- Going to the bank or post office for business
Personal commuting (home to regular workplace) is NOT deductible.
What records or documentation do I need to keep for the IRS?
Keep a mileage log of each business trip. Also, keep receipts for expenses if using the actual expense method. For the standard mileage method, only mileage logs are needed, but it’s worth keeping additional proof.
Are there any limits to how much mileage I can deduct?
There’s no dollar cap on total business mileage if the miles claimed are legitimate, properly documented, and related to your business. However, overestimating or inflating mileage can trigger an IRS audit.
What if I use my personal car for both business and personal driving?
You can deduct only the portion of miles driven for qualified business purposes. Keep a log to separate business and personal use, and claim only business mileage on your taxes.



